03 Jun Pricing2 Constant Elasticity – June’s Free MBTN Tutorial
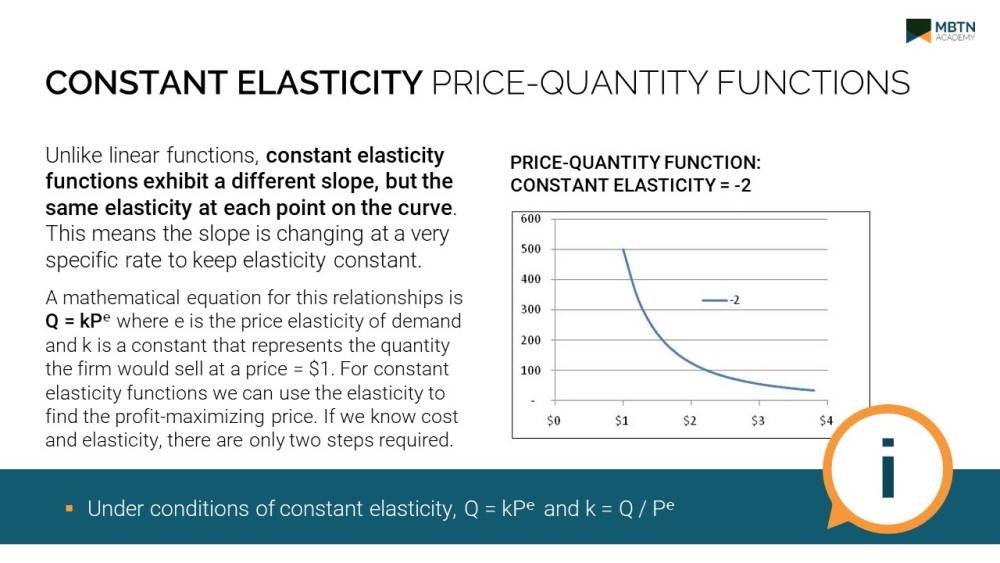
This month’s free MBTN tutorial addresses pricing decisions under conditions of constant elasticity, and is co-authored by Paul Farris and Phil Pfiefer of the Darden School of Business at the University of Virginia. Unlike linear functions, constant elasticity functions exhibit a different slope, but the same elasticity at each point on the curve. This means the slope is changing at a very specific rate to keep elasticity constant. A mathematical equation for this relationships is Q = kP℮ where e is the price elasticity of demand and k is a constant that represents the quantity the firm would sell at a price = $1. Discover how to find the profit maximizing price under these conditions in this month’s tutorial.
Pricing 2 covers the following topics:
– The relationship between price and quantity
– Elastic demand and inelastic demand
– How to calculate the optimal price under conditions of constant elasticity
The free link has expired, but check out this month’s tutorial under the Business Education Resources Blog.
If you found this topic valuable and you are faculty at a University or Community College, you might also be interested in our complete catalog of MBTN modules, available for use in academic settings. You can choose any combination of 3 or more modules to suit your needs.
Our complete catalog of MBTN modules
If you are an individual interested in learning more about Marketing Metrics and Concepts, please consider either of the following packages.
All Marketing Modules ($59.95)
MBTN All Modules and Certifications ($99.95)
Best regards,
Your Team at MBTN Academy
We hope you enjoyed this month’s tutorial on pricing decisions under conditions of constant elasticity.
Best regards,
Your Team at MBTN Academy
Follow us on Twitter, Mastodon, and LinkedIn


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.